

![]()
![]()
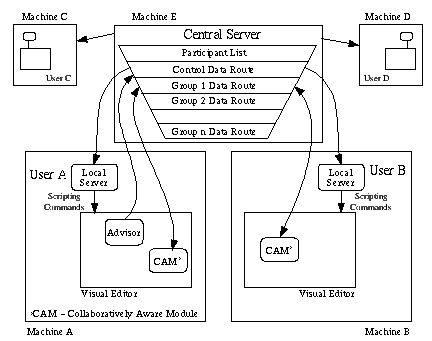
Figure 1 : Multi-user architecture
Multi-user Architecture
IRIS Explorer uses version 2.0 of the multi-user COVISA collaborative architecture. The elements of this architecture (Figure 1) are as follows:
Overview
The COVISA architecture includes a suite of modules for facilitating collaborative working within the framework of IRIS Explorer. The local server has been implemented as a module along with an Advisor module and the collaboratively aware modules for each of the internal datatypes. These behave like any other IRIS Explorer module: their names are listed in the librarian window and they are launched into the map editor and connected to other modules exactly as normal. There is no need for the user to learn any additional skills: the transition from single user to multi-user environment is seamless.
A collaborative session begins when one party launches a local server module and enters the connection details of the central server. Any collaboratively aware modules subsequently launched use information set by their local server to find and connect to the central server by means of a socket. The act of connection initiates a unique data route within the server and causes the automatic launch of corresponding modules in the other connected sessions. The architecture is designed to allow participants to join and leave during the lifetime of the session; if a party connects to an already running session then the central server automatically sends commands to the new local server enabling the new party to catch up on the current set of CAMs.
Once a CAM is connected to a data route, any data passed into it from the local session is forwarded to the central server which then distributes this data to all other group members. A group is defined as a set of identical collaboratively aware modules, one in each of the collaboratorsí environments, which are sharing a specific data object. Participants can identify shared data by means of the unique group ID attached to each module which is consistent between all participants. In addition to being able to join and leave a session in progress, participants may disconnect individual modules from the group to allow periods of independent work on a subset of the pipeline while remaining in contact with the rest of the session. Disconnected modules can be re-connected subsequently to their group and the results shared once more.
Central Server
The central server (often referred to as the COVISA Server in other parts of this documentation) is the hub of the collaborative session and is set running on a machine accessible to all participants on a known port number. It accepts connections from local servers, adding their connection details to the list of current participants, and issues a unique server ID. If required the central server creates and sends the appropriate Skm commands to the new local server to initiate the launch of CAMs corresponding to the current shared set.
In addition to maintaining the list of participants the central server is also responsible for maintaining a list of current groups and distributing data between group members. The server distinguishes the sending module by means of its local server ID and then duplicates and distributes the incoming data object to all other group members. Group members are held in a list and should two group members send data at the same time the central server propagates the data from the first member in the list and disposes of data from the second. This is done to prevent groups getting out of synchronisation. When the number of group members falls to zero the central server deletes the group from the list.
Local Server
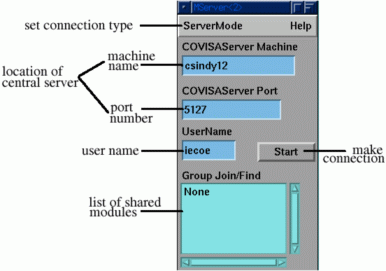
Figure 2: Local server module
The job of the local server is twofold: to establish the collaborative session by connecting to the central server, subsequently providing CAMs with this connection information; and to provide a channel for the central server to issue Skm commands to either launch new CAMs or establish pipeline fragments as directed by an Advisor module (see next section). Once launched the user enters the machine name and port number of the central server and then hits the start button (the IRIS Explorer environment defines suitable defaults which are used by the module when it is started up). The local server can connect to the central server in one of two modes: on-the-fly is used in dynamic pipeline construction with the map editor where launching a CAM causes corresponding CAM launches in other collaboratorsí environments; application is used for shrink wrapped collaborative applications where a CAM launch does not initiate a corresponding CAM launch in any other session (see End User Applications).
Advisor Module
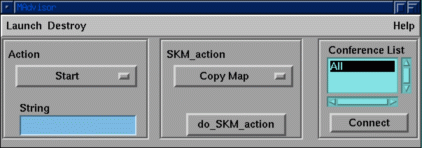
Figure 3: Advisor module
The Advisor module is used to allow one collaborator to aid another in helpdesk or educational situations when one user has more visualization experience than the other. The user with the Advisor module is able to initiate a whole pipeline or fragments of one, setting all of the parameters and making all of the wiring connections, in the other userís environment. When an Advisor module connects to the central server it is similar to a local server in that it does not cause the creation of corresponding Advisor modules in the other participantsí environments. All Skm commands generated by the Advisor module are passed to the collaboratorsí local servers which in turn pass them into the environment where they are processed. The user acting as the advisor selects modules to send by highlighting them in their own environment and then chooses to: copy the parameter set from the selected modules; copy both the wiring connections and parameter set, or; recreate the entire piece of pipeline in the collaboratorsí environments. Additionally, specific Skm commands can be entered into the Advisor module to be executed in the collaboratorsí environments. This allows the advisor greater flexibility in controlling the collaboratorís environment than is allowed by a pre-defined set of commands and is likely to be required in the helpdesk scenario.
Collaboratively Aware Modules
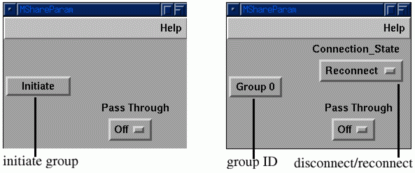
Figure 4 : Share module showing both disconnected and connected states
A set of collaboratively aware modules is provided for each of the internal datatypes. When a CAM is launched it first collects connection information from the local server giving the location of the central server, and then waits for the instruction to connect. If this instruction comes by means of the user pressing the initiate button (see Figure 4), it connects to the central server in initiate mode. This mode causes the central server to create a new group, returning the group ID to the module. If the module has been automatically launched by the central server then Skm is used to make it connect in join mode. This connection mode does not cause the creation of a new group but adds this module to the requested group. Once connected to a group a user can disconnect and re-connect the module by means of a toggle, re-connection being achieved using the join mode.